Themes and data.
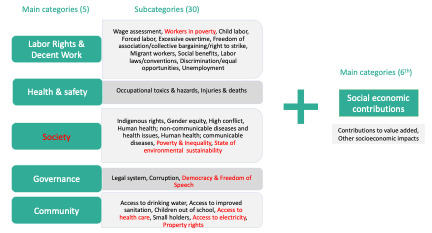
There are 244 countries and 57 economic sectors to choose from. The data comprehensively addresses social issues on human rights, working conditions, community impacts and governance issues, via a set of over 132 risk indicators grouped within 30 themes. Risks are expressed by country and sector, commodity or production activity. In the SHDB licenses 30 themes are included and some countries are grouped in regions because of the Global Trade model (140 countries and regions).